Types of Microfluidic Devices

By Sergei Chapek, Research Engineer
Microfluidics has transformed the way we study and manipulate small amounts of fluids, empowering us to make significant strides in fields like biomedical research, analytical chemistry, and diagnostics. With the emergence of 3D printing technology, the fabrication of microfluidic devices has become more accessible, customizable, and efficient.
Here are the top 5 microfluidic devices:
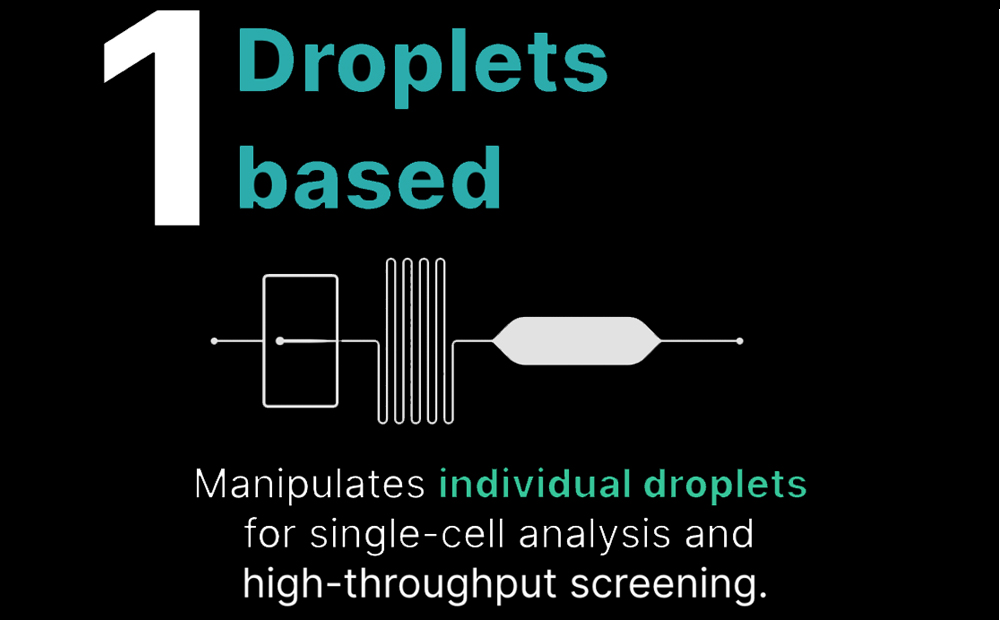
Droplet-based microfluidic devices
These devices enable the manipulation and analysis of individual droplets, which can contain cells, reagents, or other biological components. They are used for applications such as single-cell analysis, high-throughput screening, and digital PCR.

Organ-on-a-chip devices
These devices aim to mimic the structure and function of human organs by integrating living cells with microfluidic channels. They provide a platform for studying organ-level physiology, drug testing, and disease modeling in a more physiologically relevant context.

Lab-on-a-chip devices
These devices integrate multiple laboratory functions onto a single chip, enabling miniaturized and automated analysis of biological samples. They can perform tasks such as sample preparation, mixing, separation, and detection, making them useful for applications like point-of-care diagnostics and environmental monitoring.

Cell sorting devices
These devices utilize microfluidic channels and various sorting mechanisms to separate cells based on their physical or biochemical properties. They enable high-throughput and label-free cell sorting, which is valuable for applications such as cell-based assays, stem cell research, and cancer diagnostics
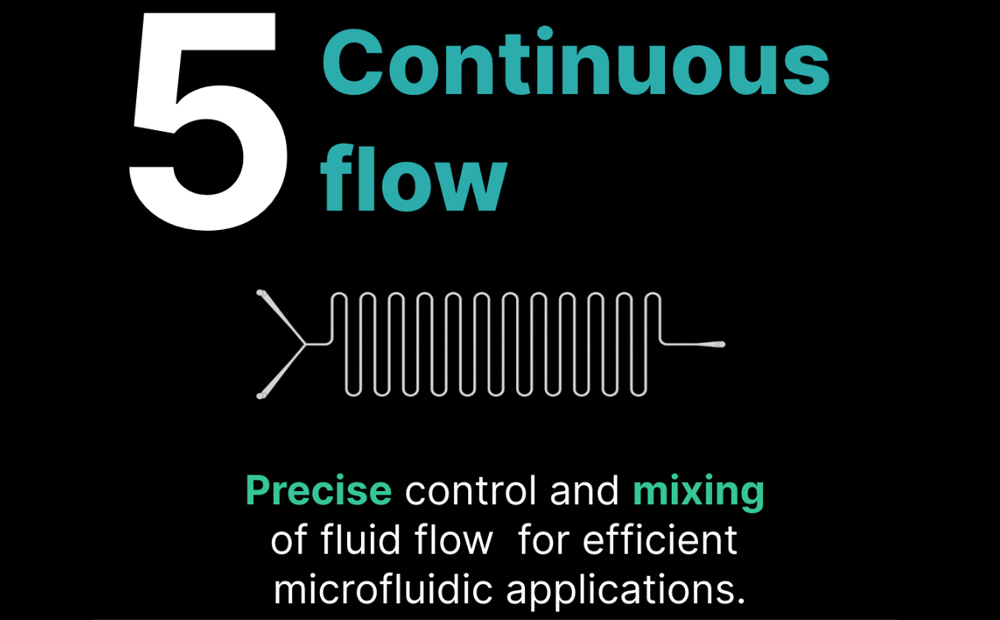
Continuous flow microfluidic devices
These devices allow continuous flow of fluids through microchannels, enabling precise control over fluid flow rates and mixing. They are used for applications such as chemical synthesis, enzymatic reactions, and cell culture, where precise fluid control and efficient mass transfer are crucial.
Share: