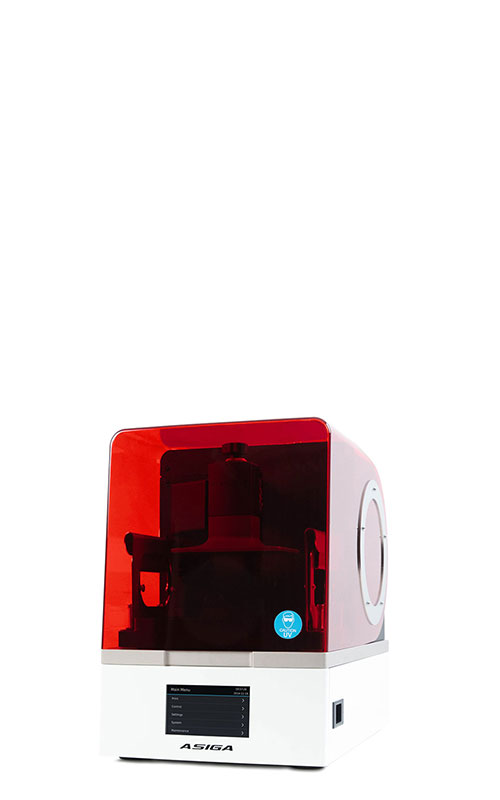
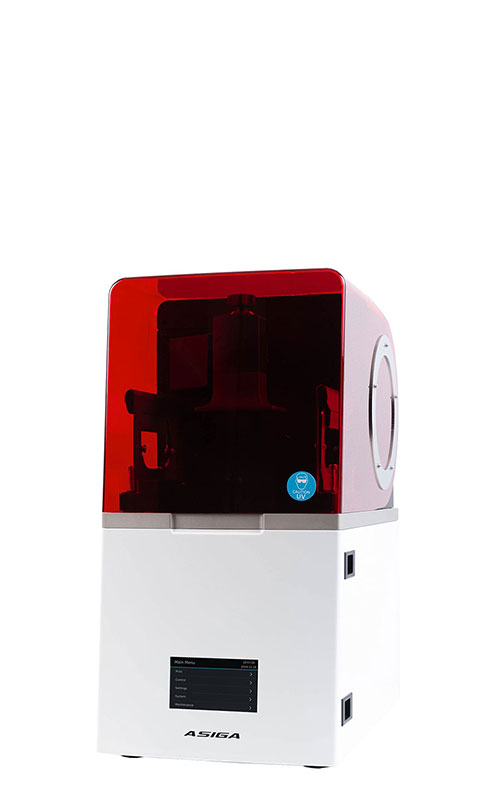
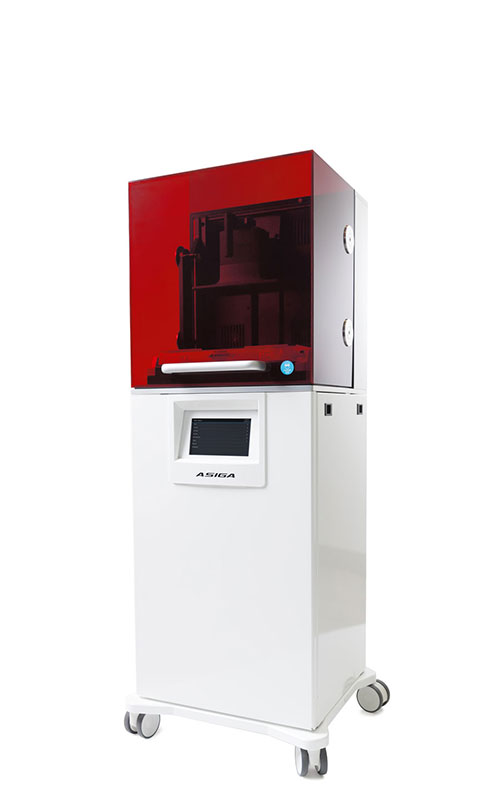
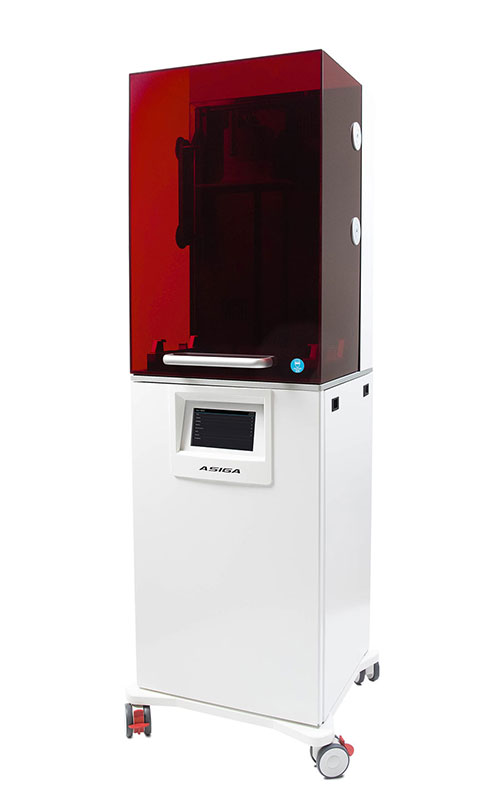
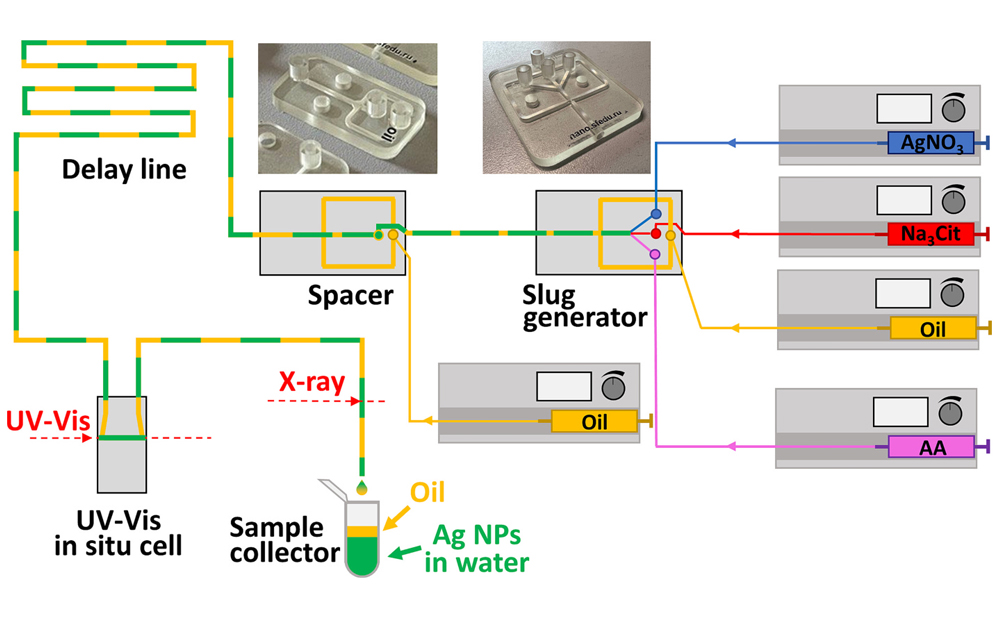
3D-printed microfluidic system for the in situ diagnostics and screening of nanoparticles synthesis parameters
Noble metal nanoparticles (NPs) find a wide range of industrial applications, including catalysis, photonics, drug delivery, medical imaging. Their unique optical properties are interesting for surface-enhanced
Raman scattering, photovoltaics, molecular detection, and photothermal cancer therapies. In a typical procedure metal nanoparticles grow in the presence of metal ions, reducing agent and stabilizer. The result of the reduction, nucleation and growth depends on many parameters, including temperature and reagent concentrations.
The human operator may unintentionally introduce variations in standard protocols by varying mixing time or speed and order of reagents that affect the resulting particle size distribution. Design of experiments approach may help to identify the role of each synthesis parameter on the resulting properties while machine learning (ML) algorithms offer a more sophisticated alternative that is capable to find complex dependencies in the highly dimensional data and apply optimization strategies.
Share: